
 |
|
ASP.NET with the Delphi LanguageYou might like it or not (I'm not that fond of it), but Microsoft's ASP technology plays a significant role in the development of web applications, as least on the Windows platform. With the transition to ASP.NET, this technology has fully embraced the .NET Framework; now, with the availability of a Delphi compiler for .NET, the Delphi language can be your language of choice in the development of ASP applications. To create a test, configure IIS to support ASP.NET (I won't cover these steps, which are beyond the scope of this book, but you can find more information on www.asp.net) and then place in the target folder the web.config file distributed by Borland along with the Delphi for .NET Preview (and available in the aspx subfolder). This configuration file defines the mapping of the language to a specific library, again provided by Borland. The core of the file (which uses XML format) has the following elements: <compilation debug="true">
<assemblies>
<add assembly="DelphiProvider" />
</assemblies>
<compilers>
<compiler language="Delphi" extension=".pas"
type="Borland.Delphi.DelphiCodeProvider,DelphiProvider" />
</compilers>
</compilation>
To test that the configuration is correct, nothing is better than trying an example. Create a new file (I've called mine aspbase.aspx, available in the DelphiAsp folder of the chapter source code) and type something like the following:
<html>
<body>
<h1>ASP.NET with Delphi</h1>
<script language="Delphi" runat="server">
procedure HelloMessage(msg: string);
var
i: Integer;
begin
for i := 2 to 7 do
Response.Write ('<font size=' + inttostr (i) +
'>' + msg + '</font> <br>')
end;
</script>
<% HelloMessage('Delphi for .NET Preview made this'); %>
</html>
</body>
The effect is to execute the Delphi code after transforming this file into a .NET source, compiling it with the Delphi preview compiler, and compiling the IL into assembly code (remember, even scripts in .NET are compiled before they are executed). If everything goes well, the browser should display output like that shown in Figure 25.3. From this point on, you can do anything an ASP.NET application provides. The only other example I want to show you is the use of controls with event handlers, which I've covered in a different situation for .NET applications based on Windows forms. This example, saved in the aspui.aspx file in the AspDelphi folder, uses HTML to define a form with a textbox (that is, an edit control) and a button, plus an output label. The button has a Delphi language event handler attached to it, which moves the user input to the label (the output of the program appears in Figure 25.4):
<html>
<body>
<h1>ASP.NET with Delphi</h1>
<script language="Delphi" runat="server">
procedure ButtonClick(Sender: System.Object; E: EventArgs);
begin
Message.Text := Edit1.Text;
end;
</script>
<form runat="server">
<asp:textbox id="Edit1" runat="server"/>
<asp:button text="Click Me!" OnClick="ButtonClick" runat="server"/>
</form>
<p><b><asp:label id="Message" runat="server" text="message"/></b></p>
</html>
</body>
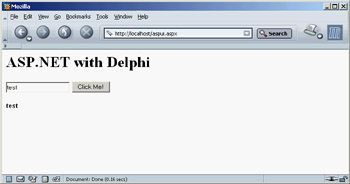
Figure 25.4: The output of the aspui.aspx example, after typing in the edit box and clicking the button This has been a limited introduction to ASP.NET with the Delphi language provider. However, it should give you a feeling for the possibilities opening up for Delphi programmers in this new world of .NET. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Copyright © 2004-2024 "Delphi Sources" by BrokenByte Software. Delphi Programming Guide |